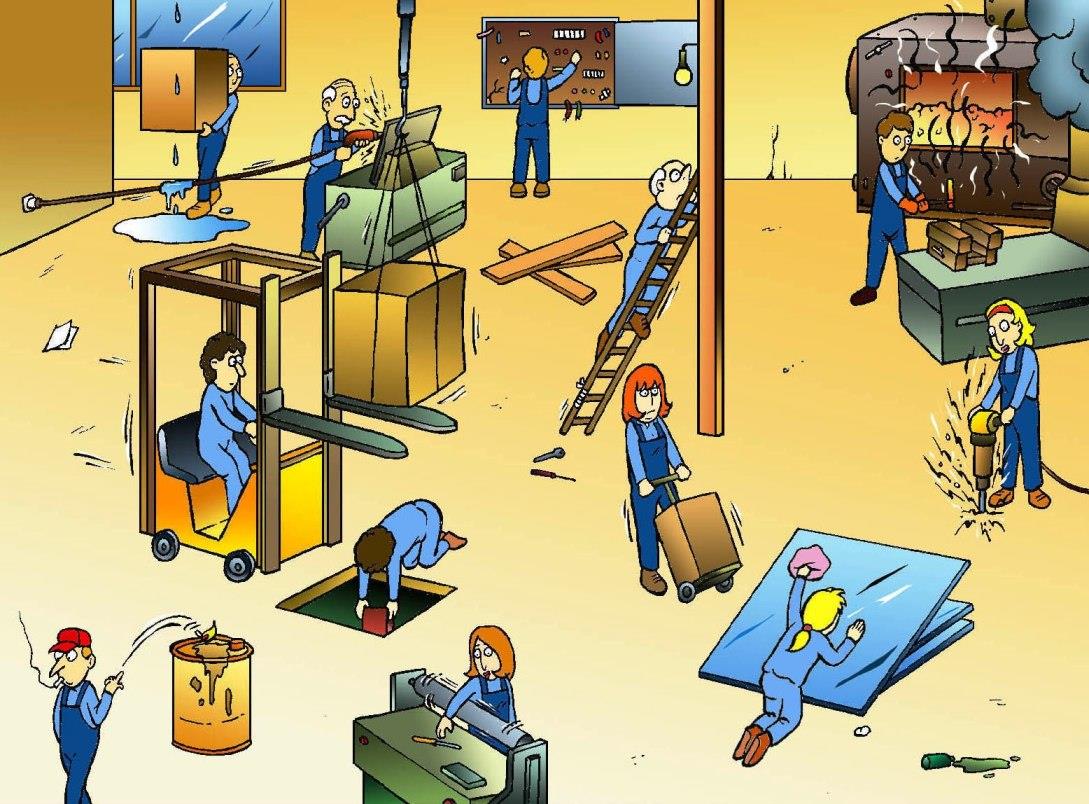
You’re about to dive into a comprehensive guide that will equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to recognize and prevent electrical hazards. Whether you’re a homeowner, a construction worker, or simply someone who interacts with electricity on a daily basis, this guide is packed with valuable information that will help you keep yourself and others safe. Within this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know about the 8 most common electrical hazards and how to mitigate them effectively. Get ready to empower yourself with the essential knowledge to navigate the electrical world safely!
Common Electrical Hazards
Electric Shock
Electric shock occurs when a person comes into contact with an electrical source, resulting in a flow of electric current through their body. This can happen due to direct contact with live electrical wires or faulty electrical appliances. Electric shock can range from mild discomfort to severe injury or even death. It is important to be aware of electrical hazards and take necessary precautions to avoid electric shock.
Electrocution
Electrocution refers to death caused by electric shock. This can occur when the electric current passing through the body is strong enough to disrupt the normal functioning of the heart or other vital organs. Electrocution can happen due to direct contact with a high-voltage power line, faulty wiring, or other electrical hazards. It is crucial to understand and address electrical hazards to prevent the risk of electrocution.
Electrical Fires
Electrical fires are a significant concern and can pose a threat to both life and property. They can occur when electrical wiring, appliances, or equipment overheat or become overloaded, igniting nearby combustible materials. Electrical fires can spread rapidly and cause extensive damage. Identifying potential electrical fire hazards and taking preventive measures is essential to minimize the risk of fires and ensure safety.
Electrical Burns
Electrical burns occur when the skin comes into contact with electricity. These burns can be caused by accidental contact with live wires or faulty electrical devices. Electrical burns can range from minor injuries to severe burns that require immediate medical attention. It is crucial to be cautious and follow safety practices to prevent electrical burns.
Overloaded Circuits
overloaded circuits can occur when too many electrical devices are connected to a single circuit, exceeding its capacity. This can result in overheating, which may lead to electrical fires. Overloaded circuits can also cause circuit breakers to trip or fuses to blow, interrupting the electrical supply. Understanding the limitations of circuits and distributing the load appropriately is vital to prevent overloading and potential hazards.
Short Circuits
Short circuits occur when a hot wire comes into contact with a neutral or ground wire, creating a low-resistance path for electrical current. This can lead to a sudden surge of electricity and cause wires to overheat and potentially ignite nearby materials. Proper wiring installation using appropriate insulation and safety measures can help prevent short circuits and minimize the risk of electrical hazards.
Frayed or Damaged Wires
Frayed or damaged wires can pose a serious electrical hazard. When wires are worn out, exposed, or damaged, they can lead to electrical fires, electric shocks, or short circuits. Aging electrical systems, rodents, or careless handling can contribute to wire damage. Regular inspection and prompt repair or replacement of frayed or damaged wires are essential to ensure electrical safety.
Improper Grounding
Improper grounding is a significant electrical hazard that occurs when electrical systems or devices are not effectively grounded. Grounding helps protect against electric shock, as it provides a pathway for the safe dissipation of electrical current into the ground. Without proper grounding, fault currents may flow through unintended paths, such as water pipes or human bodies, leading to severe injuries or electrocution. Ensuring proper grounding is a fundamental aspect of electrical safety.
Understanding Electrical Hazards
The Basics of Electricity
To comprehend electrical hazards, it is crucial to understand the basics of electricity. Electricity is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire. It powers our homes, offices, and industries, but it can also be dangerous if not handled properly. Understanding concepts like voltage, current, resistance, and power is essential to grasp how electrical hazards arise and how to prevent them.
Types of Electrical Currents
There are two primary types of electrical currents: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). AC is the most common form of current used in households and businesses, continuously changing its direction. In contrast, DC flows steadily in a single direction. Knowing the difference between AC and DC helps identify potential hazards and apply appropriate safety measures when dealing with electrical systems.
Effects of Electric Shock
Electric shock can have various effects on the human body, depending on factors such as the magnitude and duration of the current, the path it takes through the body, and individual characteristics. Mild electric shocks may cause muscle spasms, pain, and difficulty breathing, while severe shocks can lead to burns, organ damage, cardiac arrest, or death. Awareness of the potential effects of electric shock reinforces the need for electrical safety precautions.
Causes of Electrical Fires
Electrical fires can occur due to several reasons, including faulty wiring or connections, overloaded circuits, overheating appliances or equipment, and arcing or sparking. Identifying the common causes of electrical fires helps in preventing them. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and adherence to safety guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of electrical fires.
Consequences of Electrical Hazards
Electrical hazards can result in severe consequences, including serious injuries or fatalities, property damage, financial loss, and emotional trauma. Electric shock, electrocution, electrical fires, and other accidents caused by electrical hazards can have a lasting impact on individuals, families, and communities. Recognizing and understanding the consequences of electrical hazards reinforces the importance of prioritizing electrical safety in all settings.
Identifying Electrical Hazards
Electrical Outlets and Wiring
Electrical outlets and wiring can pose hazards if they are outdated, damaged, or improperly installed. Common issues include loose connections, exposed wires, faulty outlets, or incorrect grounding. Regular inspection of outlets and wiring, and addressing any issues promptly, is crucial to ensure their safe operation.
Electrical Appliances and Equipment
Electrical appliances and equipment can be hazardous if they are defective, damaged, or misused. Overheating, faulty insulation, loose or frayed wires, and improper maintenance are some potential hazards associated with appliances and equipment. Regular inspections, following manufacturer guidelines, and promptly repairing or replacing faulty items are essential to minimize the risk of electrical accidents.
Power Tools and Extension Cords
Power tools and extension cords can present electrical hazards if not used properly or if they are damaged. Tools with exposed wires, frayed cords, or faulty grounding can lead to electric shock or fires. Using appropriate extension cords, inspecting them regularly, and following safety guidelines when operating power tools are necessary precautions to prevent accidents.
Lighting and Fixtures
Lighting and fixtures, such as light bulbs, lamps, and light switches, can also pose electrical hazards. Using improper wattage bulbs, using damaged or faulty fixtures, or faulty installation can lead to electrical malfunctions. Regularly checking and maintaining lighting systems, using the correct wattage, and addressing any issues promptly can prevent electrical hazards.
Electrical Panels and Circuit Breakers
Electrical panels and circuit breakers play a crucial role in distributing electricity safely throughout a building. However, outdated or faulty electrical panels, inadequate circuit breakers, or improper wiring can lead to electrical hazards. Regular inspections, proper labeling, and timely upgrades or repairs help ensure the safe functioning of electrical panel systems.
Outdoor Electrical Hazards
Outdoor electrical hazards encompass a wide range of potential dangers, including overhead power lines, underground cables, electrical equipment in wet conditions, and damaged outdoor outlets or wiring. Awareness of outdoor electrical hazards and taking necessary precautions, such as keeping a safe distance from power lines or using weatherproof outlets, is vital to prevent accidents.
Preventing Electrical Hazards at Home
Electrical Safety Measures
Implementing electrical safety measures at home is essential to protect yourself, your family, and your property. This includes installing ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in wet areas, using surge protectors, ensuring proper grounding, and installing smoke detectors and carbon monoxide alarms. Regularly testing and maintaining these safety devices is crucial for their effectiveness.
Safe Electrical Practices
Practicing safe electrical habits is crucial to prevent hazards. This involves simple measures such as not using electrical devices with wet hands, keeping flammable materials away from outlets, avoiding overloading circuits, and using appropriate bulbs for fixtures. By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents in your home.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of electrical systems are essential to identify and address potential hazards. This includes inspecting outlets, switches, and wiring for damage, testing ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) monthly, and scheduling professional inspections to ensure the safe functioning of electrical systems. Timely repairs or upgrades based on inspection findings are vital for maintaining electrical safety.
Proper Use of Electrical Appliances
Using electrical appliances properly is crucial for safety. It is important to read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions, avoid using damaged appliances, and unplug devices when not in use. Additionally, avoiding the use of extension cords as permanent wiring and using childproof outlets to prevent accidental contact are essential practices to minimize electrical hazards.
Childproofing and Education
Childproofing your home against electrical hazards is vital to protect curious children from potential accidents. Installing outlet covers or tamper-resistant outlets, storing electrical cords out of reach, and educating children about electrical safety are key measures. Teaching children about the dangers of playing with electrical appliances or outlets can prevent accidents and ensure their safety.
Emergency Preparedness
Being prepared for electrical emergencies is crucial. This includes knowing the location of circuit breakers and how to shut off electricity in an emergency, keeping fire extinguishers readily accessible, and having a well-defined evacuation plan. Regularly reviewing and practicing emergency response procedures ensures a swift and efficient response in case of electrical incidents.
Preventing Electrical Hazards in the Workplace
Workplace Electrical Safety Regulations
Workplace electrical safety regulations exist to protect employees and maintain safe working environments. Employers must comply with relevant codes and standards set by regulatory bodies, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States. These regulations cover various aspects, including electrical equipment inspection, employee training, and safety program implementation.
Employee Training and Education
Proper training and education for employees are essential to prevent electrical hazards in the workplace. Employees should receive training on electrical safety practices, hazard recognition, correct use of equipment, safe work procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular updates and refresher training sessions reinforce good electrical safety practices and help prevent accidents.
Scheduled Equipment Inspections
Regular inspections of electrical equipment, tools, and machinery are necessary to ensure their safe operation. Employers should establish scheduled inspection routines, addressing any issues promptly. Inspections should include checking for proper grounding, examining cords and plugs for damage, and testing equipment in accordance with manufacturer guidelines or industry standards.
Proper Use and Maintenance of Tools
Using tools correctly and maintaining them properly is crucial for workplace safety. Employers should provide employees with appropriate equipment and ensure it is used as intended. Regular maintenance, including lubrication, calibration, and repairs, should be conducted according to manufacturer instructions. Encouraging employees to report any faulty equipment or tools helps maintain a safe working environment.
Electrical Safety Program Implementation
Implementing an electrical safety program in the workplace is essential for comprehensive hazard prevention. This includes developing safety policies and procedures, conducting regular risk assessments, providing personal protective equipment (PPE) as needed, and establishing clear lines of communication for reporting hazards or near-miss incidents. An effective safety program fosters a culture of awareness and accountability in the workplace.
Emergency Response to Electrical Incidents
Electric Shock First Aid
Knowing how to respond to electric shock incidents can save lives. In the event of an electric shock, it is crucial to immediately disconnect the power source, call for medical help, and perform basic first aid. This may include CPR if the person is unresponsive or providing assistance until medical professionals arrive. Properly trained personnel should be available to handle such emergencies.
Emergency Shutdown Procedures
Having well-defined emergency shutdown procedures is crucial in preventing further damage or injuries during electrical incidents. These procedures outline steps to safely shut down electricity, including turning off circuit breakers or isolating the power supply. Employees should be trained on these procedures and emergency shutdown controls should be easily accessible in the workplace.
Fire Extinguisher Usage
In the event of an electrical fire, prompt action is necessary to prevent its spread. Understanding how to use fire extinguishers safely is vital. Employees should receive training on fire extinguisher usage, including identifying the correct type of extinguisher for electrical fires (Class C), proper extinguishing techniques, and evacuation procedures when necessary.
Evacuation Protocols
In severe situations, evacuating the area may be necessary for everyone’s safety. Establishing clear evacuation protocols, including designated assembly points, evacuation routes, and communication channels, ensures a swift and organized response during electrical incidents. Regular drills and familiarization with evacuation procedures enable employees to react efficiently during emergencies.
Contacting Emergency Services
During electrical incidents, it is essential to contact emergency services promptly. This includes calling the local fire department, ambulance services, or other relevant authorities based on the severity of the situation. Providing accurate information, such as the nature of the incident and the number of injured individuals, helps emergency responders assess and address the situation effectively.
Electrical Hazard Awareness and Training
Importance of Electrical Hazard Awareness
Raising awareness about electrical hazards is crucial for preventing accidents. Educating individuals about the potential risks, consequences, and safety measures associated with electricity creates a culture of vigilance and responsibility. Promoting electrical hazard awareness at home, in the workplace, and in educational settings ensures that everyone understands the importance of electrical safety.
Regular Training and Updates
Continual training and updates on electrical safety are necessary to stay informed about new technologies, regulations, and best practices. Ongoing training helps individuals recognize hazards, apply preventive measures, and respond appropriately during emergencies. Regular updates also ensure that individuals are aware of any changes in safety standards or protocols relevant to electrical hazards.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Developing the ability to recognize warning signs of electrical hazards can save lives and prevent accidents. These signs may include flickering lights, frequent circuit breaker tripping, burning smells, buzzing sounds, or overheating electrical devices. Being observant and responsive to these warning signs enables individuals to take timely action, such as reporting hazards or seeking professional help.
Promoting a Safety Culture
Promoting a safety culture means prioritizing safety in all aspects of life. This includes actively encouraging safe practices, open communication about hazards and near-miss incidents, and recognizing and rewarding individuals for their commitment to safety. By fostering a culture of safety, individuals and organizations can collectively work towards reducing electrical hazards and creating safer environments.
Safety Standards and Codes
National Electrical Safety Codes
National electrical safety codes provide guidelines and regulations for installing, operating, and maintaining electrical systems. These codes, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States, establish minimum safety requirements for wiring, grounding, equipment, and systems. Compliance with national electrical safety codes ensures that electrical installations meet established safety standards.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Standards
OSHA standards specifically address workplace safety, including electrical safety. These standards set forth requirements for electrical equipment, safe work practices, and training. By enforcing these standards, OSHA aims to protect employees from electrical hazards in various industries and work environments. Employers must comply with OSHA regulations to ensure a safe workplace.
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standards
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) develops international standards and specifications for electrical, electronic, and related technologies. These standards cover a wide range of areas, including electrical safety, devices, equipment, and systems. Adherence to IEC standards promotes consistency and safety in electrical practices on a global scale.
Responsibilities of Individuals and Organizations
Individual Responsibility for Electrical Safety
Individuals have a responsibility to prioritize electrical safety in their daily lives. This includes using electrical devices properly, reporting hazards promptly, and educating themselves on electrical safety practices. Following safety guidelines, being aware of electrical hazards, and taking necessary precautions can help prevent accidents and protect oneself and others from harm.
Employer Responsibility for Employee Safety
Employers have a legal and moral obligation to provide a safe working environment for their employees. This includes ensuring compliance with safety regulations, providing proper training, maintaining safe equipment and systems, conducting regular inspections, and promoting a culture of safety. Employers should actively address electrical hazards and take preventive measures to protect their employees from harm.
Government Regulations and Oversight
Government regulations play a crucial role in ensuring electrical safety. Regulatory bodies, such as OSHA, establish and enforce standards to protect employees and the public from electrical hazards. These regulations aim to prevent accidents, promote safe practices, and hold individuals and organizations accountable for maintaining electrical safety.
Electrical Contractors and Manufacturers
Electrical contractors and manufacturers have a responsibility to prioritize safety in their work. Contractors should follow proper installation and maintenance practices, while manufacturers should design and produce electrical equipment adhering to safety standards. By fulfilling their responsibilities, contractors and manufacturers contribute to reducing electrical hazards and ensuring the safety of end-users.
Latest Technological Advancements in Electrical Safety
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) and Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs)
Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) and arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) are advanced safety devices that help prevent electrical accidents. GFCIs monitor the flow of electricity and can quickly detect imbalances or ground faults, automatically interrupting the circuit to prevent electric shock. AFCIs can detect dangerous arcing caused by damaged wires or faulty connections and shut off the power, reducing the risk of electrical fires.
Smart Electrical Panel Systems
Smart electrical panel systems utilize advanced technology to monitor and control electrical systems remotely. These systems can provide real-time data on energy usage, detect abnormalities, and send alerts for potential hazards. Smart electrical panel systems offer greater control and awareness, facilitating proactive measures to prevent electrical accidents and improve energy efficiency.
Electrical Safety Devices and Sensors
Various electrical safety devices and sensors are available to enhance safety. These include tamper-resistant outlets, arc fault detectors, ground fault indicators, current-limiting devices, and voltage detectors. These devices help identify potential electrical hazards, provide early warnings, and automatically shut off power in case of abnormalities, significantly reducing the risk of accidents.
Electrical Safety Monitoring Systems
Electrical safety monitoring systems provide comprehensive monitoring and analysis of electrical systems to ensure ongoing safety and reliability. These systems can track electrical consumption, detect power quality issues, identify faulty equipment or wiring, and detect potential hazards. By continuously monitoring electrical systems, potential hazards can be detected and addressed proactively, preventing accidents and improving overall system performance.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing electrical hazards are crucial for personal safety, property protection, and the well-being of communities. By recognizing common electrical hazards, understanding their causes and consequences, and implementing preventive measures, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, injuries, and property damage. Adopting comprehensive electrical safety practices, following safety standards and codes, and staying informed about technological advancements ensures a safer environment for everyone.