In the world of electrical systems and appliances, failures can occur for a multitude of reasons, disrupting our daily lives. From flickering lights to malfunctioning appliances, identifying the primary cause of these electrical failures becomes essential in order to find effective solutions. However, amidst all the potential culprits, one stands out as the most common cause of electrical failure. This article will shed light on this prevalent issue, providing insights into its impact and the necessary steps to mitigate its effects, ensuring a safe and uninterrupted power supply in our homes and workplaces.
Identifying the Primary Cause of Electrical Failures
Understanding Electrical Failures
Electrical failures refer to any malfunction or breakdown in an electrical system that results in a loss of power or damage to the system. These failures can occur due to several reasons, and understanding them is crucial for effective troubleshooting and prevention.
Importance of Identifying the Primary Cause
Identifying the primary cause of electrical failures is essential because it allows for targeted solutions and preventive measures. By determining the root cause, you can prevent recurrence, optimize maintenance practices, reduce costs, and ensure safety in electrical systems.
Common Causes of Electrical Failures
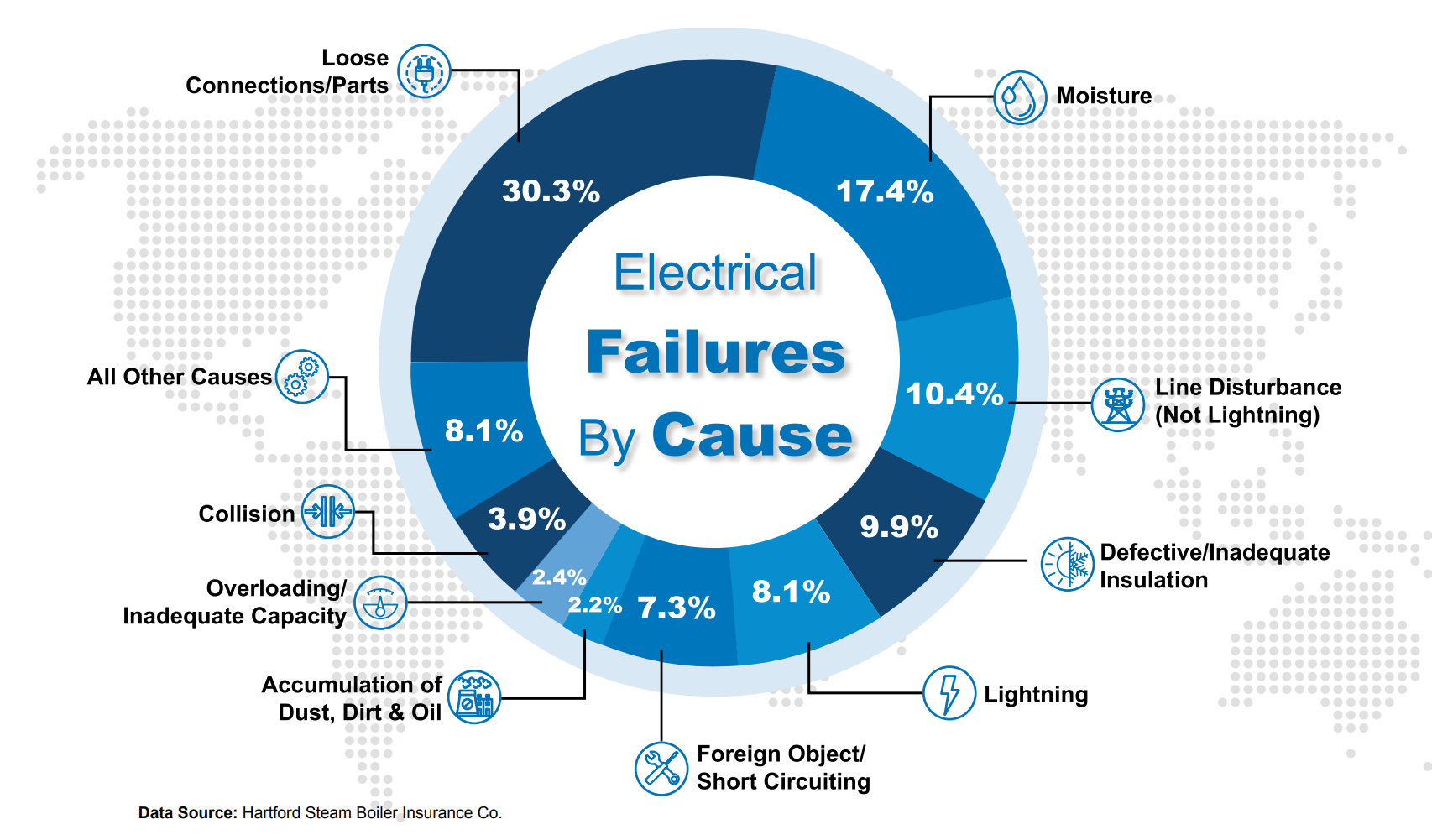
several factors can contribute to electrical failures, and familiarizing yourself with these common causes can help you address them effectively. Some of the most frequent causes include equipment aging, electrical overloads, short circuits, electrical wiring issues, power surges, corrosion, moisture damage, faulty connections, insulation breakdown, and voltage fluctuations.
Testing and Inspections
Regular testing and inspections are important in identifying potential causes of electrical failures. By conducting routine equipment testing, periodic inspections, thermal imaging assessments, voltage measurements, and ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) testing, you can identify any underlying issues in the electrical system and take appropriate action.
Safety Measures
implementing safety measures is crucial to prevent electrical failures and protect individuals and property from potential hazards. Proper grounding and bonding, circuit protection devices, electrical panel maintenance, proper labeling and documentation, and regular electrical training play a vital role in maintaining a safe electrical system.
Equipment Faults
Equipment faults can also contribute to electrical failures. worn-out components, mechanical failures, defective parts, manufacturer’s defects, and improper installation can all lead to electrical system malfunctions. Identifying these faults and addressing them promptly is essential to avoid further damage.
Overloading
Overloading is another major cause of electrical failures. When electrical circuits are overloaded with more current than they can handle, it can result in circuit breakers tripping or fuses blowing, leading to a loss of power. Understanding the causes of overloading and implementing preventive measures such as proper circuit sizing can help mitigate this issue.
Poor Maintenance
Neglected or improper maintenance practices can significantly contribute to electrical failures. Lack of regular inspections, neglected repairs, dust and dirt accumulation, loose or damaged connections, inadequate lubrication, and general wear and tear can all lead to system failures. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance and prevent electrical failures.
Detecting the Primary Cause of Electrical Failures
Detecting the primary cause of electrical failures requires a systematic approach. Thorough analysis and investigation of the problem, reviewing maintenance records, consulting experts in the field, and utilizing diagnostic tools can help pinpoint the exact cause. The elimination process, ruling out potential causes one by one, can lead to the identification of the primary cause.
Understanding Electrical Failures
Electrical failures occur when there is a disruption or breakdown in the normal functioning of an electrical system. These failures can manifest in various ways, such as sudden power loss, flickering lights, tripped circuit breakers, or burning smells. understanding the different types of electrical failures and their consequences is crucial in addressing and preventing such issues.
Definition of Electrical Failure
An electrical failure can be defined as any event or situation that impairs the functionality of an electrical system, resulting in a loss of power or damage to the system itself. It can occur at any point in the electrical system, including power generation, distribution, or consumption. electrical failures can range from minor disruptions to catastrophic events that can cause accidents, fires, or even fatalities.
Types of Electrical Failures
There are various types of electrical failures, each with its own distinct characteristics and causes. Some common types of electrical failures include open circuits, short circuits, ground faults, overloads, voltage sags or spikes, and arcing. Each type of failure requires specific troubleshooting techniques and preventive measures to mitigate them effectively.
Consequences of Electrical Failures
Electrical failures can have severe consequences, both in terms of human safety and property damage. Inadequate electrical supply can disrupt essential services, such as communication systems, healthcare facilities, and industrial operations. Additionally, electrical failures can result in electrical shock, damage to electrical equipment or appliances, fires, and even loss of life. Identifying and addressing the root cause of electrical failures is crucial to prevent such consequences.
Preventing Recurrence
Identifying the primary cause of electrical failures is vital for preventing recurrence. Once the underlying issue is determined, appropriate corrective measures can be taken to fix the problem and ensure it does not happen again. This can involve replacing faulty components, upgrading equipment, redesigning electrical systems, implementing preventive maintenance practices, or providing additional training to personnel.
Optimizing Maintenance
Identifying the primary cause of electrical failures also helps in optimizing maintenance practices. By understanding the root cause, maintenance activities can be focused on the areas prone to failures, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively. This targeted approach allows for better allocation of time, effort, and budget, ultimately leading to a more efficient and reliable electrical system.
Cost Reduction
Determining the primary cause of electrical failures can result in significant cost reductions. By addressing the underlying issue properly, the need for frequent repairs, replacements, emergency interventions, and downtime can be minimized. This results in reduced maintenance and repair costs, increased equipment lifespan, and improved overall productivity.
Ensuring Safety
The primary cause of electrical failures is often related to safety hazards. Identifying and rectifying the root cause helps in ensuring a safe electrical system. By eliminating faulty equipment, fixing improper installations, addressing wiring issues, and implementing proper protective measures, the risk of electrical accidents, injuries, or fatalities is significantly reduced. Prioritizing safety is essential for the well-being of individuals and the protection of property.
Equipment Aging
One of the most common causes of electrical failures is equipment aging. Over time, electrical components and systems deteriorate, leading to decreased performance, reliability, and safety. The wear and tear of electrical equipment can result in insulation breakdown, corrosion, loose connections, and compromised electrical performance.
Electrical Overloads
Electrical overloads occur when too much current flows through an electrical circuit, surpassing its rated capacity. This can happen due to excessive power demand, inadequate circuit sizing, or the operation of multiple high-power consuming devices simultaneously. Overloading can lead to overheating, tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses, and, in severe cases, fires or electrical system damage.
Short Circuits
A short circuit occurs when a low-resistance path is created between two conductors, resulting in a sudden surge of current. Short circuits commonly happen due to damaged insulation, faulty wiring, or accidental contact between live wires. The excessive current flow can cause circuit breakers to trip, electrical equipment to malfunction, and in extreme cases, sparks, fires, or explosions.
Electrical Wiring Issues
Incorrect or faulty electrical wiring is a prevalent cause of electrical failures. Poor workmanship, improper connections, loose or frayed wires, and insufficient insulation can lead to intermittent power loss, voltage fluctuations, overheating, or even electrical fires. Regular inspections and maintenance of electrical wiring are crucial to identify and rectify any issues promptly.
Power Surges
Power surges are sudden increases in electrical voltage and can occur due to lightning strikes, utility grid issues, or internal factors within the electrical system. These surges can damage sensitive electrical equipment, such as computers, televisions, or appliances, leading to malfunction or complete failure. Installing surge protection devices can help mitigate the impact of power surges and safeguard valuable equipment.
Corrosion
Corrosion in electrical systems can occur due to exposure to moisture, chemicals, or environmental conditions. Corrosion can result in increased resistance in electrical connections, poor conductivity, and thus, electrical failures. Regular maintenance and protection measures, such as corrosion-resistant materials and proper sealing, can help prevent corrosion-related failures.
Moisture Damage
Moisture intrusion in electrical systems can cause significant damage. Water or moisture can deteriorate insulation, corrode conductors, promote short circuits, and compromise the overall integrity of the electrical system. Detecting and addressing sources of moisture, implementing proper waterproofing measures, and regular inspections are vital to preventing moisture-related failures.
Faulty Connections
Loose, damaged, or improperly installed electrical connections can lead to electrical failures. Faulty connections can generate excessive heat, cause voltage drops, or increase resistance in the electrical circuit. Regular inspections and maintenance to ensure tight connections are essential in preventing failures caused by poor connections.
Insulation Breakdown
Insulation breakdown occurs when the insulation materials surrounding electrical conductors degrade or fail, resulting in electrical failures. Factors such as age, overloading, exposure to high temperatures, or physical damage can contribute to insulation breakdown. Regular inspections, testing, and timely replacement of deteriorated insulation are essential preventive measures.
Voltage Fluctuations
Unstable or fluctuating voltage can cause electrical failures. Voltage fluctuations can result from utility grid issues, power factor imbalances, or excessive load demands within the electrical system. These fluctuations can damage sensitive equipment, disrupt operations, or cause premature failure of electrical components. Voltage stabilization techniques and proper load management can help mitigate the risks associated with voltage fluctuations.
Regular Equipment Testing
Regular equipment testing is essential in detecting potential causes of electrical failures. Equipment testing involves conducting specific diagnostic tests to assess the performance, functionality, and integrity of electrical components, instruments, and systems. These tests can identify faulty components, deteriorated insulation, or other issues that could lead to electrical failures.
Periodic Inspections
Periodic inspections of the electrical system play a crucial role in identifying potential causes of failures. Electrical inspections involve a comprehensive assessment of the entire system, including wiring, connections, equipment, and safety measures. Through inspections, issues such as loose connections, faulty components, or inadequate maintenance can be discovered and addressed promptly.
Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses infrared technology to identify variations in temperature. This technique can detect hotspots caused by loose connections, overloading, or equipment malfunctions. By conducting regular thermal imaging assessments, potential causes of electrical failures can be identified before they escalate into major issues.
Voltage Measurements
Voltage measurements involve checking the voltage levels at different points within the electrical system. This helps identify abnormal voltage fluctuations, imbalances, or excessive voltage drops that could lead to electrical failures. Regular voltage measurements can assist in detecting potential causes and taking preventive actions.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Testing
GFCI testing is crucial in identifying faults in electrical systems that can cause ground faults or electrical shocks. GFCI devices are designed to monitor the electrical current flowing through a circuit and quickly interrupt the power supply if a fault is detected. Regular testing ensures the proper functioning of GFCI devices and the prevention of electrical failures due to ground faults.
Proper Grounding and Bonding
Proper grounding and bonding are essential safety measures in electrical systems. Grounding provides a pathway for electrical current to flow safely to the ground, protecting individuals and equipment from electrical shocks. Bonding ensures that all conductive parts of a system are electrically connected, preventing potential differences and electrical failures. Implementing and maintaining proper grounding and bonding practices is vital for a safe electrical system.
Circuit Protection Devices
Circuit protection devices, such as circuit breakers and fuses, are crucial in preventing electrical failures caused by overloads, short circuits, or ground faults. These devices are designed to interrupt the electrical current flow when abnormal conditions are detected, protecting the electrical system and preventing damage or accidents. Regular maintenance and testing of circuit protection devices ensure their proper functioning.
Electrical Panel Maintenance
Regular maintenance of electrical panels is necessary to prevent failures and ensure optimal performance. Electrical panels house circuit breakers, fuses, and other protective devices, and their proper operation is crucial for the overall reliability and safety of the electrical system. Maintenance tasks include cleaning, tightening connections, inspecting for signs of corrosion or damage, and verifying proper labeling.
Proper Labeling and Documentation
Proper labeling and documentation of electrical systems facilitate troubleshooting, maintenance, and emergency response procedures. Clear and accurate labeling helps identify circuits, equipment, components, and potential hazards. Detailed documentation ensures that maintenance activities, repairs, and modifications are recorded, allowing for historical analysis and effective future planning.
Regular Electrical Training
Regular electrical training and education for personnel involved in the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of electrical systems are essential. Training ensures that individuals understand the potential causes of electrical failures, proper safety procedures, and best practices in maintenance. Well-trained personnel are better equipped to detect, prevent, and address electrical failures, improving system reliability and safety.
Worn Out Components
As electrical equipment ages, its components can wear out, leading to potential failures. Components such as capacitors, resistors, switches, and contacts can degrade over time, resulting in reduced performance or complete breakdown. Regular inspections and replacement of worn-out components are crucial in preventing failures caused by aging equipment.
Mechanical Failures
Mechanical failures in electrical systems occur when mechanical parts or mechanisms fail to operate as intended. Examples include a motor’s bearings seizing or a circuit breaker’s mechanical linkage malfunctioning. These failures can result in electrical system malfunctions, loss of power, or damage to equipment. Regular maintenance and inspections help identify and rectify mechanical failures.
Defective Parts
Defective parts in electrical systems can cause failures even in relatively new equipment. Manufacturing defects, substandard materials, or improper assembly can lead to premature failure of electrical components or systems. Ensuring the use of high-quality, reliable components and conducting thorough inspections before installation can help minimize the risk of failures due to defective parts.
Manufacturer’s Defects
Sometimes, electrical failures can be traced back to manufacturer’s defects. Errors in design, production, or quality control can result in faulty equipment or components that are more prone to failures. Manufacturers should adhere to industry standards, conduct adequate testing, and implement quality assurance processes to prevent defects that could lead to electrical failures.
Improper Installation
Improper installation of electrical equipment or systems can lead to various failures. This includes errors in wiring, incorrect connections, inadequate grounding, or insufficient clearance for heat dissipation. Proper installation practices, following manufacturer guidelines and industry standards, are essential to prevent failures caused by installation-related issues.
Understanding Overloading
Overloading occurs when electrical circuits are subjected to excessive current flow, surpassing their rated capacity. This can happen when the total power demand exceeds the circuit’s capability or when multiple high-power consuming devices are operated simultaneously. Overloading can lead to overheating, tripping of circuit breakers or blowing of fuses, and equipment malfunction.
Causes of Overloading
There are several causes of overloading in electrical systems. Inadequate circuit sizing, where the capacity of the circuit does not match the load requirements, is a common cause. Other causes include using extension cords or power strips with insufficient capacity, adding new equipment without considering the available power supply, or operating multiple high-power devices simultaneously.
Preventing Overloading
Preventing overloading requires careful planning and consideration of the power demands and available electrical capacity. Proper circuit sizing, based on the anticipated load, is crucial. Avoiding the use of extension cords for long-term or high-power applications and evenly distributing the power load across multiple circuits can also help prevent overloading. Regular monitoring of power consumption and load balancing can further assist in identifying potential overloading situations.
Proper Circuit Sizing
Proper circuit sizing is essential in preventing overloading. When installing electrical circuits, it is crucial to calculate the anticipated load and select the appropriate wire size, circuit breaker rating, and conduit size. Undersized circuits can result in frequent tripping of circuit breakers, overheating, and premature failure of electrical components. Consulting electrical codes and industry standards is advisable when determining circuit sizes.
Lack of Regular Inspections
Lack of regular inspections is a common cause of electrical failures. Without periodic assessments of electrical systems, underlying issues can go undetected, leading to potential failures. Regular inspections provide an opportunity to identify loose connections, deteriorated insulation, or worn-out components before they cause malfunctions or accidents. Implementing a scheduled inspection program is crucial for early detection and prevention of failures.
Neglected Repairs
Neglecting repairs or delaying necessary maintenance can contribute to electrical failures. Equipment or components that require repair or replacement should be addressed promptly to prevent further deterioration or system malfunctions. Neglected repairs can lead to increased resistance in electrical connections, insulation breakdown, or mechanical failures, all of which can result in failures or accidents.
Dust and Dirt Accumulation
Accumulation of dust and dirt on electrical equipment can obstruct airflow and cause overheating. Dust or dirt particles can settle on electrical contacts, interfering with proper electrical conduction and leading to intermittent failures. Regular cleaning and maintenance, such as blowing out dust, wiping surfaces, and vacuuming, help prevent failures caused by dust and dirt accumulation.
Loose or Damaged Connections
Loose or damaged electrical connections can result in increased resistance, arcing, or even electrical shocks. Temperature fluctuations, vibrations, or improper installation practices can contribute to connection issues. Regular inspections to ensure tight and secure connections, repairing or replacing damaged connectors, and using proper torque during installation are essential in preventing failures due to loose or damaged connections.
Inadequate Lubrication
Inadequate lubrication of moving parts in electrical equipment can cause friction, increased wear, and eventual failure. Proper lubrication is crucial for maintaining the performance and longevity of mechanical components such as motors, bearings, and switches. Following manufacturer guidelines for lubrication procedures, regular inspections, and lubricant replacement are necessary preventive measures.
Wear and Tear
The normal wear and tear of electrical components and systems can contribute to failures. As electrical equipment ages, its performance and reliability can decrease. Over time, electrical connections can loosen, insulation can deteriorate, and mechanical parts can wear out. Implementing regular inspections, maintenance, and equipment replacement programs is vital to detect and prevent failures due to wear and tear.
Thorough Analysis and Investigation
Detecting the primary cause of electrical failures requires a thorough analysis and investigation. As failures can be complex and involve multiple factors, carefully examining the circumstances, symptoms, and possible contributing factors is necessary. This analysis can involve reviewing event logs, gathering data, speaking with personnel involved, and conducting visual inspections to identify potential causes.
Reviewing Maintenance Records
Maintenance records provide valuable insights into the history of an electrical system and can shed light on potential causes of failures. Reviewing maintenance records allows for the identification of any recurring issues, patterns of failure, or missed opportunities for preventive maintenance. These records help pinpoint areas for improvement, identify potential causes, and develop appropriate action plans.
Consulting Experts
When faced with challenging electrical failures, consulting experts in the field can provide valuable expertise and guidance. Electrical engineers, technicians, or consultants with specialized knowledge and experience can assist in identifying the primary cause, conducting in-depth assessments, and recommending appropriate solutions. Their expertise can help ensure a comprehensive and accurate diagnosis of failures.
Using Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools play a crucial role in detecting the primary cause of electrical failures. Advanced tools, such as power quality analyzers, thermal imaging cameras, insulation testers, or oscilloscopes, allow for thorough testing, measurements, and analysis of electrical systems and components. These tools provide valuable data and visual representations, aiding in the identification of underlying issues.
Elimination Process
Detecting the primary cause of electrical failures often involves an elimination process. By systematically ruling out potential causes one by one, the underlying issue can be identified. This process may involve conducting specific tests, inspections, or analyses to narrow down the possibilities until the root cause is identified. The elimination process ensures a methodical and systematic approach to problem-solving.
- Tags:
- Failures
- Identifying
- Primary Cause