In this article, we will explore the key differences between house wiring and industrial wiring. Whether you’re a homeowner or a curious individual looking to expand your knowledge, understanding these distinctions is essential. While both types of wiring share similarities, such as the use of electrical circuits and safety precautions, there are several crucial aspects that set them apart. By gaining insights into the distinctive characteristics of house and industrial wiring, you’ll be better equipped to ensure electrical safety and make informed decisions for your specific needs.
Overview
Definition of house wiring
House wiring refers to the electrical wiring system within a residential property, including single-family homes, apartments, and condominiums. It involves the installation of electrical wires, outlets, switches, and fixtures to provide electrical power throughout the house. House wiring is designed to meet the electrical demands of everyday residential activities, such as lighting, heating, cooling, and powering household appliances.
Definition of industrial wiring
Industrial wiring, on the other hand, pertains to the electrical infrastructure found in commercial and industrial buildings. This includes factories, warehouses, office buildings, and other large-scale facilities. Industrial wiring is designed to handle higher electrical loads and more complex electrical systems, as it needs to power machinery, equipment, and a multitude of electrical devices that are crucial for industrial operations.
Purpose
Residential requirements
The purpose of house wiring is to provide safe and reliable electrical power to residential properties. It ensures that homeowners have access to electricity for lighting, heating, cooling, cooking, entertainment, and various other household activities. House wiring also involves the provision of adequate electrical outlets and circuits to meet the needs of modern homes, ensuring that there are sufficient power sources in every room.
Industrial requirements
Industrial wiring serves the critical purpose of providing power to commercial and industrial buildings, where the demands on the electrical system are much higher than in residential settings. It facilitates the operation of large machinery, HVAC systems, lighting for warehouses and production areas, communication systems, and other essential equipment necessary for industrial processes. Industrial wiring must be robust and capable of supporting heavy electrical loads to ensure uninterrupted operations.
Wiring Standards
Residential electrical codes
Residential electrical codes are specific regulations and standards that govern the installation, design, and maintenance of electrical systems in residential buildings. These codes ensure that house wiring is performed safely and in compliance with established guidelines. They cover aspects such as the placement of outlets, the use of grounding, the maximum number of devices per circuit, and the type of wiring materials to be used. Compliance with residential electrical codes is essential to prevent electrical hazards and promote safety within homes.
Industrial electrical codes
Industrial electrical codes, on the other hand, are a set of guidelines and regulations that govern the installation, design, and maintenance of electrical systems in commercial and industrial buildings. These codes prioritize safety and reliability, given the higher electrical loads and more complex systems present in industrial settings. They address factors such as electrical distribution, grounding, circuit protection, specialized equipment requirements, and emergency power systems. Adhering to industrial electrical codes is crucial to prevent accidents, equipment failures, and production downtime.
Voltage Requirements
Residential voltage limitations
Residential electrical systems typically operate on a single-phase power supply, with a standard nominal voltage ranging from 110 to 120 volts in North America and 220 to 240 volts in other parts of the world. These voltage levels are considered safe for domestic use and cater to the electrical demands of lighting, appliances, and other household devices.
Industrial voltage requirements
Industrial electrical systems, on the other hand, often require higher voltage levels to accommodate the power demands of heavy machinery and equipment. Depending on the specific industrial application, voltage levels can range from 208 to 480 volts for three-phase power. These higher voltage requirements allow for better efficiency in powering industrial processes and ensure that the electrical system can meet the demands of industrial equipment.
Load Capacity
Residential load capacity
The load capacity of a residential electrical system is determined by the size and capacity of its electrical service panel. It refers to the maximum amount of electrical power that can be safely drawn from the system without overloading it. Residential load capacity is usually measured in amperes (amps) and is typically lower than that of an industrial system. The load capacity of a residential system is designed to handle the simultaneous operation of various household appliances and devices without overburdening the electrical system.
Industrial load capacity
Industrial electrical systems need to be capable of supporting much higher load capacities due to the substantial power requirements of industrial machinery and equipment. The load capacity of an industrial system is significantly larger than that of a residential system and is typically measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA) or megavolt-amperes (MVA). Industrial load capacity is carefully calculated to ensure that the electrical system can handle the simultaneous operation of multiple heavy-duty machines and devices without causing overheating or electrical failures.
Circuit Design
Residential circuit design
In residential circuit design, the electrical system is divided into circuits that serve specific areas or rooms within the house. These circuits are designed to accommodate the electrical load requirements of each area, ensuring that there are an adequate number of outlets and switches, and that the circuit capacity is not exceeded. Residential circuits are usually designed with a combination of lighting circuits, general-purpose circuits, and dedicated circuits for high-power appliances such as air conditioning units and electric stoves.
Industrial circuit design
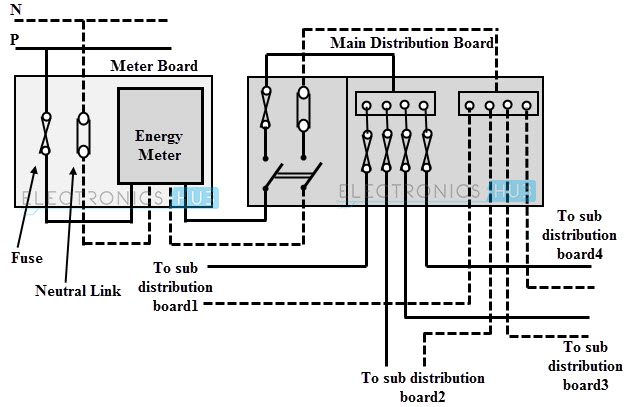
Industrial circuit design is more complex and extensive compared to residential circuit design due to the larger scale of industrial facilities and the power requirements of industrial machinery. Industrial electrical systems are typically divided into multiple electrical distribution panels or switchboards that supply electricity to different sections of the facility. Circuits are carefully planned based on the electrical load requirements of each area, ensuring that the power distribution is balanced and that there are adequate backup systems, such as motor control centers or substations, to ensure uninterrupted power supply.
Installation Process
Residential installation process
The installation of house wiring typically begins during the construction phase of a residential property. It involves the routing of electrical cables, wires, and conduits through the walls, ceilings, and floors, connecting them to the main electrical service panel. Electricians follow specific wiring diagrams and blueprints to ensure that the wiring is properly installed, safely grounded, and adequately insulated. Installation also includes mounting electrical outlets, switches, light fixtures, and other devices throughout the house according to the electrical plans.
Industrial installation process
Industrial wiring installation involves more complex and specialized processes compared to residential wiring. It often requires the expertise of qualified industrial electricians who are familiar with the unique challenges of industrial settings. The installation process begins with planning and designing the electrical system based on the specific requirements of the industrial facility. Electricians then install raceways, conduits, and cable trays to route the electrical cables and wires. They also install and connect switchgear, transformers, motor control centers, and other electrical components necessary for the industrial operations. Industrial installations adhere to strict safety protocols and are subject to inspections and testing before being commissioned.
Materials and Components
Residential wiring materials
Residential wiring typically involves the use of copper or aluminum conductors, insulated with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) for safety. Electrical cables or wires are commonly used for power distribution, along with flexible cords for connecting appliances. Residential installations also include electrical outlets and switches made from durable materials such as thermoplastics. The choice of materials ensures the longevity and safety of the residential electrical system.
Industrial wiring materials
Industrial wiring requires materials that can withstand harsher environments and higher electrical loads. Copper conductors are commonly used due to their excellent electrical conductivity and durability. However, in some cases, aluminum conductors are used for cost-effectiveness. Industrial wiring often involves the use of larger gauge cables, sometimes shielded or armored to protect against mechanical damage or electromagnetic interference. Industrial installations also include heavy-duty switchgear, motor control equipment, and other specialized components designed to meet the demands of industrial operations.
Safety Considerations
Residential safety precautions
Safety is paramount in residential wiring installations. Electricians follow specific safety protocols to minimize the risk of electrical hazards and ensure the safety of homeowners. These include proper grounding, the use of circuit breakers, ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), and arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) to protect against electrical shocks and fires. Adequate insulation and correct cable sizing are crucial to prevent overheating and electrical failures. Residential electrical systems also incorporate smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors to enhance safety within the home.
Industrial safety precautions
Industrial wiring installations prioritize safety due to the higher risks involved in industrial environments. Special attention is given to electrical grounding and bonding to prevent electrostatic discharge and mitigate the potential for electrical explosions. Additional safety measures such as motor overload protection, thermal protection devices, and emergency shutdown systems are implemented to safeguard equipment and personnel. Industrial facilities often have more stringent safety regulations in place, and regular maintenance, inspections, and employee training are essential to ensure a safe working environment.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Residential maintenance and troubleshooting
Regular maintenance of a residential electrical system is crucial to prevent potential hazards and ensure its smooth operation. Homeowners should regularly check for loose connections, damaged or frayed wiring, and signs of overheating such as discolored outlets or switches. It is advisable to schedule periodic inspections by a licensed electrician to identify any potential issues and address them promptly. Troubleshooting in residential settings often involves identifying and replacing faulty devices, checking for tripped circuit breakers, and addressing any electrical issues that may arise.
Industrial maintenance and troubleshooting
Industrial electrical systems require regular maintenance to ensure their reliability and prevent costly downtime. Maintenance activities may include visual inspections, electrical testing, and maintenance of electrical equipment, such as motor bearings, thermal protection devices, and contactors. Regular calibrations and inspections of protective devices, such as relays, circuit breakers, and transformers, are necessary to ensure the system’s proper functioning. Troubleshooting in industrial settings involves using specialized tools and equipment to pinpoint electrical failures, replace faulty components, and ensure the continuous operation of critical machinery. Proper documentation and record-keeping are also important for tracking maintenance activities and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
In conclusion, while both house wiring and industrial wiring serve the purpose of providing electrical power, there are significant differences between them. House wiring focuses on meeting the electrical needs of residential properties, adhering to specific codes and standards for safety and practicality. Industrial wiring, on the other hand, caters to the power demands of complex industrial operations, requiring higher voltage levels, larger load capacities, and specialized materials and components. Understanding these distinctions is essential for the safe and efficient provision of electrical power in both residential and industrial settings.